Abstract
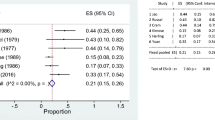
In a prospective study, 37 consecutive patients with radiation-induced proctosigmoiditis were randomized to receive a four-week course of either 3.0 g oral sulfasalazine plus 20 mg twice daily rectal prednisolone enemas (group I,N=18) or 2.0 g twice daily rectal sucralfate enemas plus oral placebo (group II,N=19). The two groups were comparable with respect to demographic features, duration of symptoms, and clinical and endoscopic staging of the disease. Fifteen patients in group I and 17 in group II completed the trial. At four weeks, both groups showed significant clinical improvement (P<0.01 for group I andP<0.001 for group II) and endoscopic healing (P<0.01 for group I andP<0.001 for group II). When the two groups were compared, sucralfate enemas showed a significantly better response as assessed clinically (P<0.05), although endoscopically the response was not statistically different (P>0.05). We conclude that both treatment regimens are effective in the management of radiation proctitis. Sucralfate enemas give a better clinical response, are tolerated better, and because of the lower cost should be the preferred mode of short-term treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham IGE: The management of radiation proctitis. Aus NZ J Surg 50:172–178, 1980
Deitel M, Vasic V: Major intestinal complications of radiotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol 72:65–70, 1979
Gilinsky NH, Burns DG, Barbezat GO, Levin W, Myers HS, Marks IN: The natural history of radiation-induced proctosigmoiditis: An analysis of 88 patients. Q J Med 52:40–53, 1983
Goldstein F, Khoury J, Thorton JJ: Treatment of chronic radiation enteritis and colitis with salicylazosulfapyridine and systemic corticosteroids. Am J Gastroenterol 65:201–208, 1976
Kochhar R, Sharma SC, Gupta BB, Mehta SK: Rectal sucralfate in radiation proctitis. Lancet 2:400, 1988
Galland RB, Spencer J: Surgical aspects of radiation injury to the intestine. Br J Surg 66:135–138, 1979
Cooke SAR, De Moor NG: The surgical treatment of radiation damaged rectum. Br J Surg 68:488–492, 1981
Buchi KN, Dixon JA: Argon laser treatment of hemorrhagic proctitis. Gastrointest Endosc 33:27–30, 1987
Baum CA, Biddle WL, Miner PB: Failure of 5-aminosalicylic acid enemas to improve chronic radiation proctitis. Dig Dis Sci 34:758–760, 1989
Batman F, Arslan S, Telatar H: Effect of sucralfate in the treatment of solitary rectal ulcer. Endoscopy 20:128, 1988
Kochhar R, Aggarwal R, Dhar A, Patel F, Mehta SK: Sucralfate enema in ulcerative recto-sigmoid lesions. Dis Colon Rectum 33:49–51, 1990
Spiliadis C, Skandalis N, Emmanouilidis A: Treatment of solitary rectal ulcer syndrome with sucralfate enema. Gastrointest Endosc 35:131–132, 1989
Carling L, Kagevi I, Borvall E: Sucralfate enema—effective in IBD? Endoscopy 18:115, 1986
Bronner MH, Yantis PL: Intracolonic sucralfate suspension for postpolypectomy hemorrhage. Gastrointest Endosc 32:362–363, 1986
Danesh BJG, Duncan A, Russell RI: Is an acid pH medium required for the protective effect of sucralfate against mucosal injury? Am J Med 83(suppl 3B):11–13, 1987
Zahavi I, Avidor I, Marcus H, Rosenbach Y, Waisman Y, Ligumsky M, Dinari G: Effect of sucralfate on experimental colitis in the rat. Dis Colon Rectum 32:95–98, 1989
Floman Y, Zor U: Mechanism of steroid action in inflammation: inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and release. Prostaglandins 12:403–413, 1976
Sharon P, Ligumsky M, Rachmilewitz D, Zor U: Role of prostaglandins in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology 75:638–640, 1978
Haboubi NY, Schofield PF, Rowland PL: The light and electron microscopic features of early and late phase radiation induced proctitis. Am J Gastroenterol 83:1140–1144, 1988
Singleton JW, Law DH, Kelley ML, Mekhjian HS, Sturdevant RAL: National Cooperative Crohn's disease study: Adverse reactions to study drugs. Gastroenterology 77:870–872, 1979
Lee DAH, Taylor GM, James VHT, Walker G: Plasma prednisolone levels and adrenocortical responsiveness after administration of prednisolone-21-phosphate as a retention enema. Gut 20:349–355, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kochhar, R., Patel, F., Sharma, S.C. et al. Radiation-induced proctosigmoiditis. Digest Dis Sci 36, 103–107 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300096
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300096